Flora Folium: Plant Leaf Identification Using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
Author's Country: Philippines
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36805/cgwb2584Keywords:
Convolutional Neural Network;, Deep Learning;, Image Processing;, Leaf Identification;, Plants;Abstract
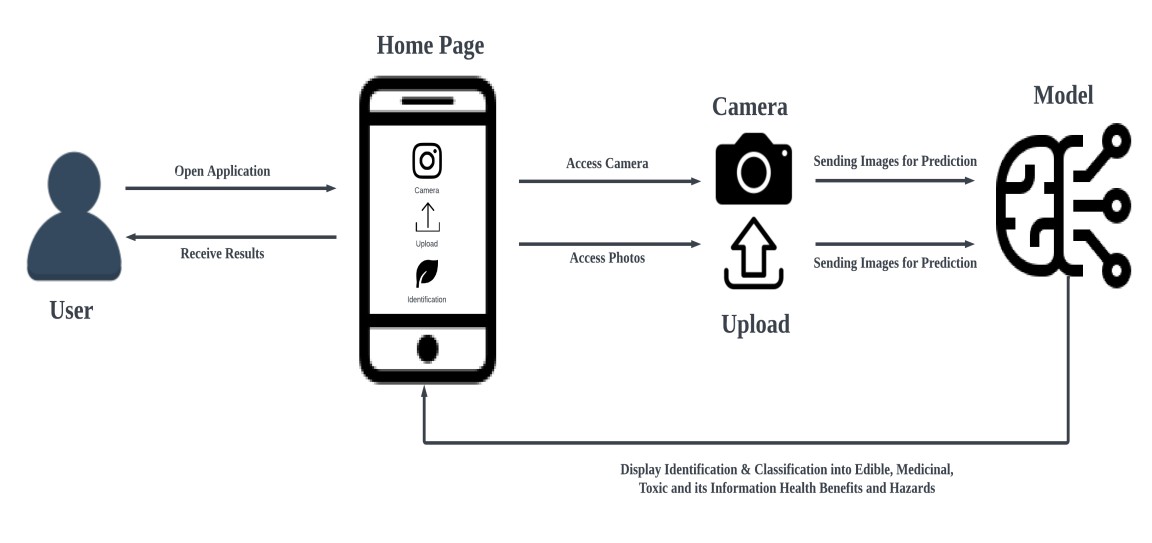
Image processing is a technique to translate an image into digital form and execute some operations on it to obtain an improved image or extract some useful information from it. FloraFolium aimed to address the challenges in plant identification, especially in the Philippines, where many plant species are not well-studied or properly recorded. Many people struggle to tell which plants are edible, medicinal, or toxic because of limited access to official guides and reliable information. To solve this problem, the FloraFolium project created a mobile application that uses Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to identify plant leaves and classify them into three categories: edible, medicinal, or toxic. The system was tested and evaluated based on ISO 25010 software quality standards. The results showed high ratings for functionality, usability, and efficiency, making the app reliable for everyday use. While the app performed well, some areas, like security and reliability in unusual conditions, need improvement. The study also found that the image quality greatly affects the system's accuracy. A balanced dataset of 15,000 images was divided into 80% for training and 20% for testing/validation. The model achieved a test accuracy of 99% and an overall validation accuracy of 98.8%, with the best weights saved at epoch 20 during the 30-epoch training period. The FloraFolium app is a helpful tool for outdoor enthusiasts, gardeners, farmers, and anyone interested in learning more about plants. It can also help preserve traditional knowledge about medicinal plants
Downloads
References
[1] Taslim, A. S. (2021). Plant leaf identification system using convolutional neural network. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics,, 10, 3341-3352. doi:https://doi.org/10.11591/EEI.V10I6.2332.
[2] Alassafi, M.O.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Naseem, I.; AlGhamdi, R.; Alotaibi, R.; Kateb, F.A.; Oqaibi, H.M.; Alshdadi, A.A.; Yusuf, S.A. A novel deep learning architecture with image diffusion for robust face presentation attack detection. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 59204–59216.
[3] Tan, Z.; Liu, A.; Wan, J.; Liu, H.; Lei, Z.; Guo, G.; Li, S.Z. Cross-batch hard example mining with pseudo large batch for id vs. spot face recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3224–3235.
[4] Sheikhjafari, A.; Krishnaswamy, D.; Noga, M.; Ray, N.; Punithakumar, K. Deep learning-based parameterization of diffeomorphic image registration for cardiac image segmentation. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2023, 22, 800–807.
[5] Felt, V.; Kacker, S.; Kusters, J.; Pendergrast, J.; Cahoy, K. Fast Ocean front detection using deep learning edge detection models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4204812.
[6] Zhang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Song, M.; Yu, H. Combined deep priors with low-rank tensor factorization for hyperspectral image restoration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 5500205.
[7] Luna, R. G., Rosales, M. A., & Dadios, E. P. (2019). Classification of philippine herbal plants via leaf using different machine learning algorithms. Journal of Computational Innovations and Engineering Applications, 29-34.
[8] Rosales, Eunice & Amistad, Vanessa & Picardal, Jay. (2019). Floristic Inventory and Ethnobotany of Wild Edible Plants in Cebu Island, Philippines. Asian Journal of Biodiversity. 9. 90-114. 10.7828/ajob.v9i1.1236.
[9] Dapar, M.L.G., Alejandro, G.J.D., Meve, U. et al. Quantitative ethnopharmacological documentation and molecular confirmation of medicinal plants used by the Manobo tribe of Agusan del Sur, Philippines. J Ethnobiology Ethnomedicine 16, 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-020-00363-7
[10] Berihu, M., Fang, J., & Lu, S. (2022). Automatic Classification of Medicinal Plants of Leaf Images Based on Convolutional Neural Network. SpringerLink, 108-116.
[11] Taslim, A., Saon, S., Muladi, M., & Hidayat, W. N. (2021). Plant leaf identification system using convolutional neural network. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 10(6), 3341-3352.
[12] Salka, T. D., Hanafi, M. B., Rahman, S. M. S. A. A., Zulperi, D. B. M., & Omar, Z. (2025). Plant leaf disease detection and classification using convolution neural networks model: a review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 58(10), 322.
[13] Thanjaivadivel, M., Gobinath, C., Vellingiri, J., Kaliraj, S., & Femilda Josephin, J. S. (2025). EnConv: enhanced CNN for leaf disease classification. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 132(1), 32.
[14] Ali, H., Shifa, N., Benlamri, R., Farooque, A. A., & Yaqub, R. (2025). A fine-tuned EfficientNet-B0 convolutional neural network for accurate and efficient classification of apple leaf diseases. Scientific Reports, 15(1), 25732.
[15] Paul, H., Udayangani, H., Umesha, K., Lankasena, N., Liyanage, C., & Thambugala, K. (2025). Maize leaf disease detection using convolutional neural network: a mobile application based on pre-trained VGG16 architecture. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 53(2), 367-383.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Lisensi Creative Commons Atribusi-BerbagiSerupa 4.0 Internasional.



